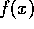 has a minimum entropy is selected
i.e.
has a minimum entropy is selected
i.e.
The first stage of the algorithms consists in selecting for analysis a segment of a signal of length N. A group of libraries and bases, say for example the sampling basis, the Fourier basis, the Haar-Walsh wavelet-packets, various QMF Daubechies filters defining smoother wavelet packets, local trigonometric adapted windows in both frequency and time, etc.
A basis in which the signal 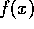 has a minimum entropy is selected
i.e.
has a minimum entropy is selected
i.e.

where  are the orthogonal waveforms in the selected ``best basis''
for which
are the orthogonal waveforms in the selected ``best basis''
for which

is minimal.
We recall that  is a measure of concentration of the
expansion while
is a measure of concentration of the
expansion while 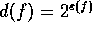 , called the theoretical dimension
represents the ``number'' of ``free'' parameters present in the signal
, called the theoretical dimension
represents the ``number'' of ``free'' parameters present in the signal

is the theoretical rate of ``compression'' achieved by the expansion
in  ,
,  .
.